Tetra-amelia syndrome vs robert syndrome
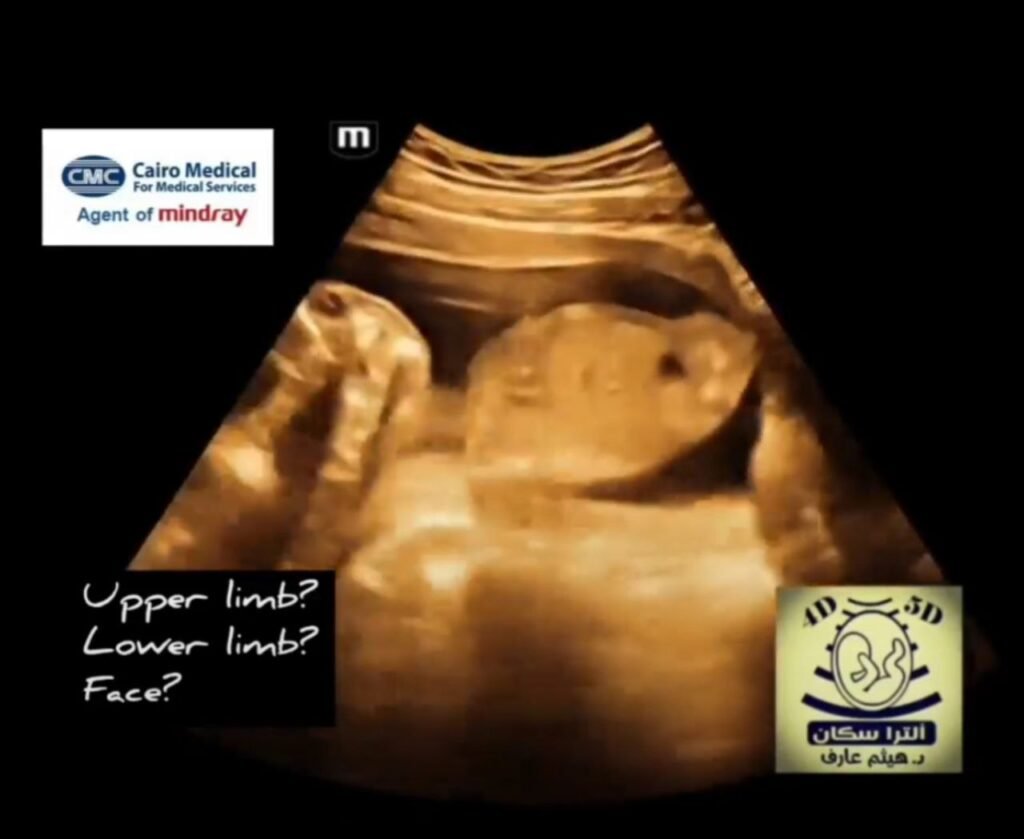

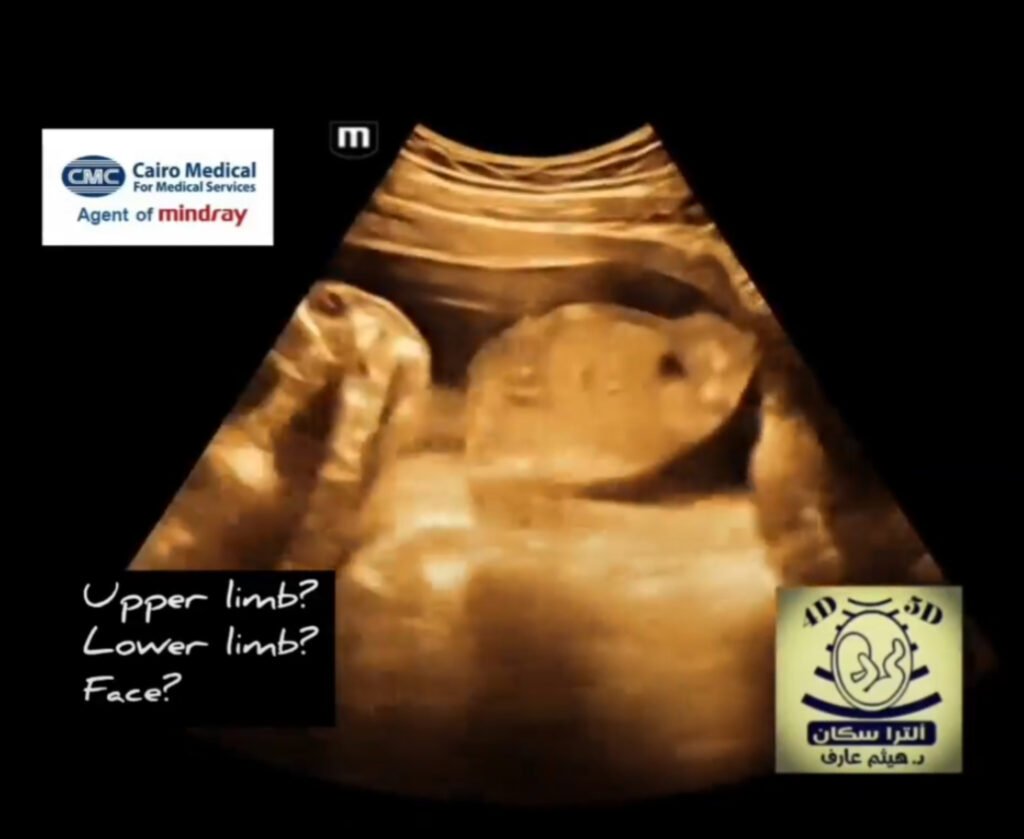
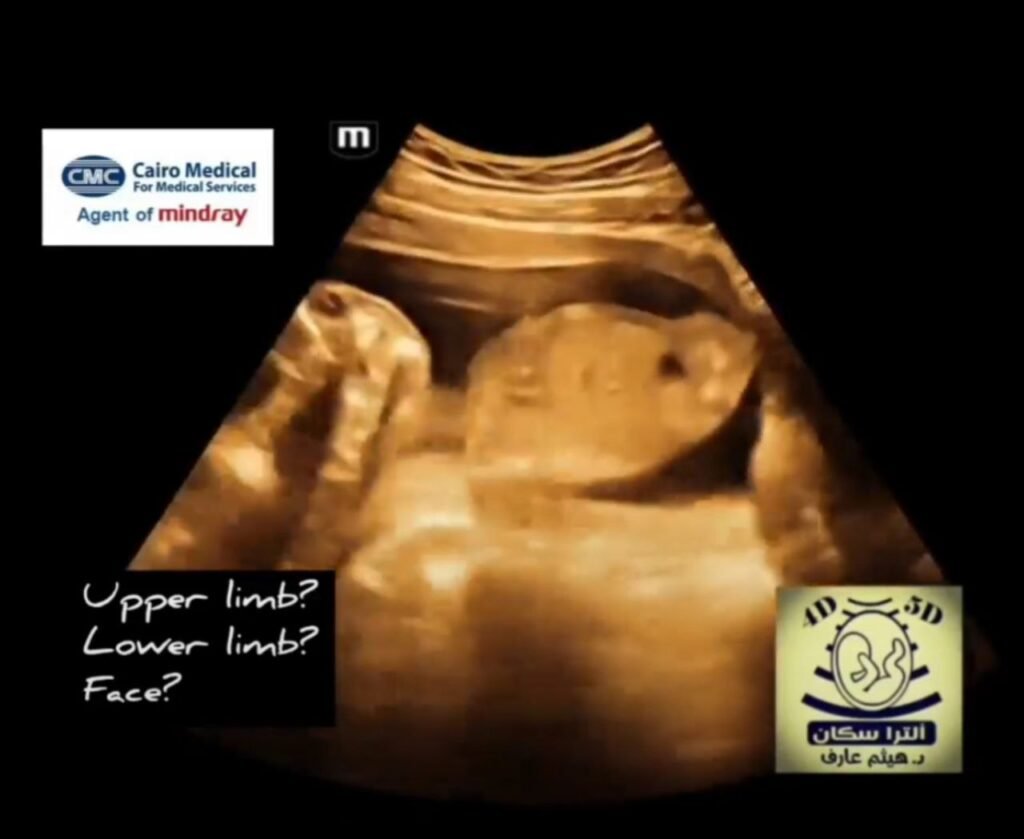
Tetra-amelia SyndromeDefinition:A condition characterized by the complete absence of all four limbs (tetra = four, amelia = absence of a limb). Associated Anomalies:Can occur in isolation or with other congenital anomalies, such as facial clefts and lung hypoplasia. Genetic Cause:While not fully understood, some cases are linked to mutations in the WNT3 gene, suggesting a specific genetic basis. Prognosis:Often associated with stillbirth or early death due to the severity of the medical problems. Roberts SyndromeDefinition:An autosomal recessive disorder marked by variable severity of limb shortening (phocomelia), midfacial clefting, and other anomalies. Key Feature:A hallmark is premature separation of chromosomes at the centromere, leading to abnormal cell division and malformations. Presentation:Limb deficiencies can be severe, with some cases resembling tetra-amelia, though the underlying mechanism is distinct. Associated Anomalies:Includes facial clefts, small chin (micrognathia), and ear abnormalities. Prognosis:Varies, with some severely affected pregnancies resulting in early death, while mildly affected individuals can live into adulthood. Key DifferencesDefining Characteristic:Tetra-amelia is the absence of limbs, whereas Roberts syndrome is characterized by premature chromosome separation and associated malformations, including limb shortening. Chromosomal Finding:A definitive feature of Roberts syndrome is the defect in chromosome centromere division, a finding absent in tetra-amelia. Genetic Basis:Tetra-amelia is linked to WNT3 gene mutations, while Roberts syndrome involves errors in the process of cell division.

