غير مصنف
Bilateral duplex collecting system fetal ultrasound with bilateral ureteroceles a case report
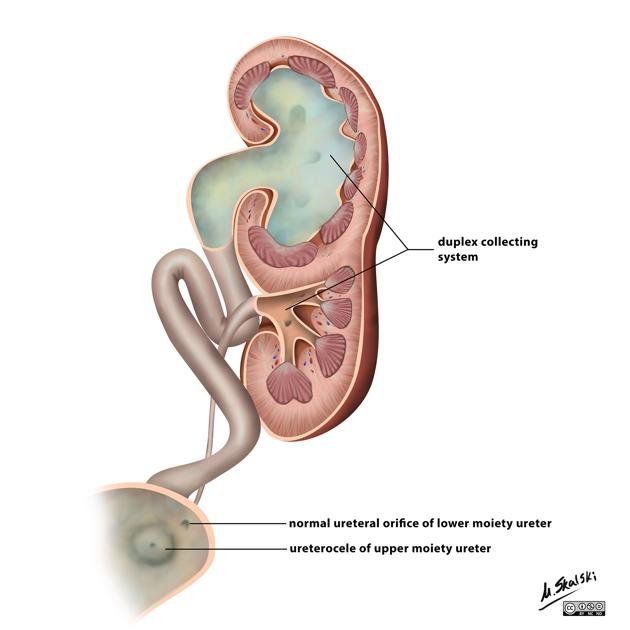
duplex collecting system (or duplex kidney) is a common congenital variant where a single kidney has two separate drainage systems. It occurs in approximately 1% of the general population and is more frequent in females.
Key Ultrasound Findings
Diagnosis typically relies on seeing two non-communicating renal pelves in a single kidney, often best visualized in a longitudinal view.
- “Figure-of-Eight” Sign: Early prenatal scans (14–16 weeks) may show the kidney shaped like a figure eight due to two separate poles and pelves.
- Asymmetric Hydronephrosis: One pole (usually the upper) may appear dilated while the other remains normal.
- Ureterocele: A cystic, anechoic structure within the fetal bladder, often associated with the upper pole ureter.
- Kidney Size: The affected kidney may measure larger than normal, often exceeding the 95th percentile for gestational age.
Clinical Significance & Rules
- Weigert-Meyer Rule: In complete duplication, the upper pole ureter typically obstructs (leading to hydronephrosis or ureterocele), while the lower pole ureter is prone to reflux (back-flow of urine).

